
These current assets must also be converted to cash in time to pay the company’s obligations when they come due. Since no interest is owed as of December 31, 2024, no liability for interest is reported on this balance sheet. However, some accounting rules do require some recorded costs to be reduced through a contra asset account.
Consulting services
Because payment is due within a year, investors and analysts are keen to ascertain that a company has enough cash on its books to cover its short-term liabilities. Total liabilities are all the financial obligations owed by one party to another individual or entity that haven’t yet been paid. It might signal weak financial stability if a company has had more expenses than revenues for the last three years because it’s been losing money for those years. In accounting, financial liabilities are linked to past transactions or events that will provide future economic benefits. Not surprisingly, a current liability will show up on the liability side of the balance sheet. In fact, as the balance sheet is often arranged in ascending order of liquidity, the current liability section will almost inevitably appear at the very top of the liability side.
How Data Management Strategies Are Shaping the Future of Business

Instead, any sales taxes not yet remitted to the government is a current liability. Accounts payable represents the amounts owed to vendors or suppliers for goods or services the company had received on credit. The amount is supported by the vendors’ invoices which had been received, approved for payment, and recorded in the company’s general ledger account Accounts Payable. In the U.S., a company can elect which costs will be removed first from inventory list of long term liabilities (oldest, most recent, average, or specific cost). During times of inflation or deflation this decision affects both the cost of the inventory reported on the balance sheet and the cost of goods sold reported on the income statement.
- Provincial Sales Tax (PST) is the provincial sales tax paid by the final consumers of products.
- Then the total reserves would be $(11000+80000+95000) or $285,000 after the third Financial Year.
- They are of two types namely, preference shareholders and equity shareholders.
- They’re not just numbers on a balance sheet—they reflect how a business plans for growth, fulfills promises to employees and customers, and navigates financial challenges.
- For example, a corporation may issue $1 million in bonds with a 5% interest rate due in ten years.
Current portion of long-term debt

A loan is another form of long-term debt that a corporation can use to finance its operations. Like bonds, loans can be secured, giving the lender the right https://riberadelcalderon.com/actualidad/bookkeeping/corporation-definition-types-advantages-and-legal/ to specified assets of the corporation if the debt cannot be repaid. For instance a mortgage is a loan secured by specified real estate of the company, usually land with buildings on it.
- Till then, the liability is treated as the deferred tax, which is repayable within the next financial year.
- Long term liabilities are financial obligations that your company does not have to pay immediately.
- So while Long-Term Assets include Fixed Assets, the two are not synonymous.
- This line item is in constant flux as bonds are issued, mature, or called back by the issuer.
- For example, the preferred stockholders will be paid dividends before the common stockholders receive dividends.
Pepsi’s Long-Term Debt Example
The average time it takes for a retailer’s or manufacturer’s inventory to turn to cash. If a manufacturer turns its inventory six times per year (every two months) and allows customers to pay in 30 days, its operating cycle is approximately three months. Some valuable items that cannot be measured and expressed in dollars include the company’s outstanding reputation, its customer base, the value of successful consumer brands, and its management team. As a result these items are not reported among the assets appearing on the balance sheet. You should consider our materials to be an introduction to selected accounting and bookkeeping topics (with complexities likely omitted). We focus on financial statement reporting and do not discuss how that differs from income tax reporting.
- These are borrowed sums that your business agrees to repay over time, typically with interest.
- In short, a company needs to generate enough revenue and cash in the short term to cover its current liabilities.
- Non-current liabilities which are also known as long term liabilities.
- They provide financing for operations and growth, but they also create risk.

It is common for bonds to mature (come due) years after the bonds were issued. Other accrued expenses and liabilities is a current liability that reports the amounts that a company has incurred (and therefore owes) other than the amounts already recorded in Accounts Payable. A short-term loan payable is an obligation usually in the form of a formal written promise to pay the principal amount within one year of the balance sheet bookkeeping date. Short-term loans payable could appear as notes payable or short-term debt. Current liabilities are a company’s obligations that will come due within one year of the balance sheet’s date and will require the use of a current asset or create another current liability. Assets are recorded in the company’s general ledger accounts at their cost when they were acquired.
- Each corporation issuing bonds has unique financing needs and attempts to satisfy various borrowing situations and investor preferences.
- As well, a loan does not give rise to a premium or discount because it is obtained at the market rate of interest in effect at the time.
- While both represent obligations a business must fulfill, the key distinction lies in their payment timelines and how they affect financial planning.
- The current portion of long-term debt is the principal portion of any long-term debt that is due within the upcoming 12 month period.
- Liabilities can include future services owed, short-term or long-term loans, or unsettled obligations from past transactions.
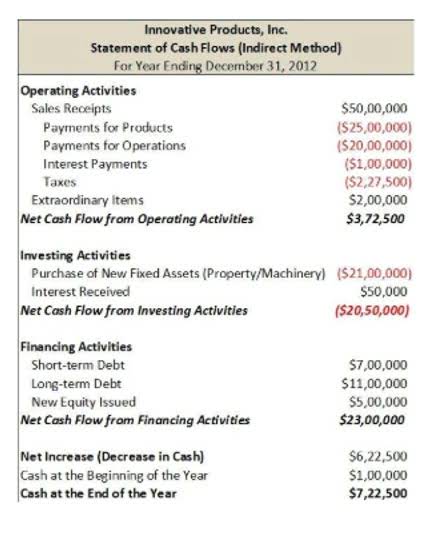
Entries are passed when obtaining funds, accruing interest, and during repayments. On a balance sheet, long-term liabilities are shown under the ‘Non-Current Liabilities’ section below current liabilities. Detailed disclosures are often given in the notes to accounts as per accounting standards and regulatory norms. Investors and financial agencies as well as creditors and analysts look at your long term liabilities or debt. They use these numbers recorded on your financial statements to judge business solvency.







Leave a Reply